4.3.5 Users and ACL
In designing users and ACLs (Access Control Lists), it is necessary to consider what permissions are needed in the creation of users, groups, and roles. A user’s operating permissions are determined by the role’s access rights, which are assigned directly or indirectly through groups or other roles.
(Table) User and ACL design items and outline
| Item | Definition method | Key design points |
|---|---|---|
| ・User ・Group ・Role |
GUI | Create and assign users, groups, and roles. |
| ・ACL | YAML file | Consider the scope of access to the UI, applications, etc. for users, groups, and roles. ACLs can only be assigned directly to roles. |
| ・GitRole | GUI | Consider the scope of access to the repository for users assigned to the group. |
| ・Roles In This Organization | GUI | Consider the scope of access that each AWX organization provides to its users. |
For details on user management settings, see “User management”.
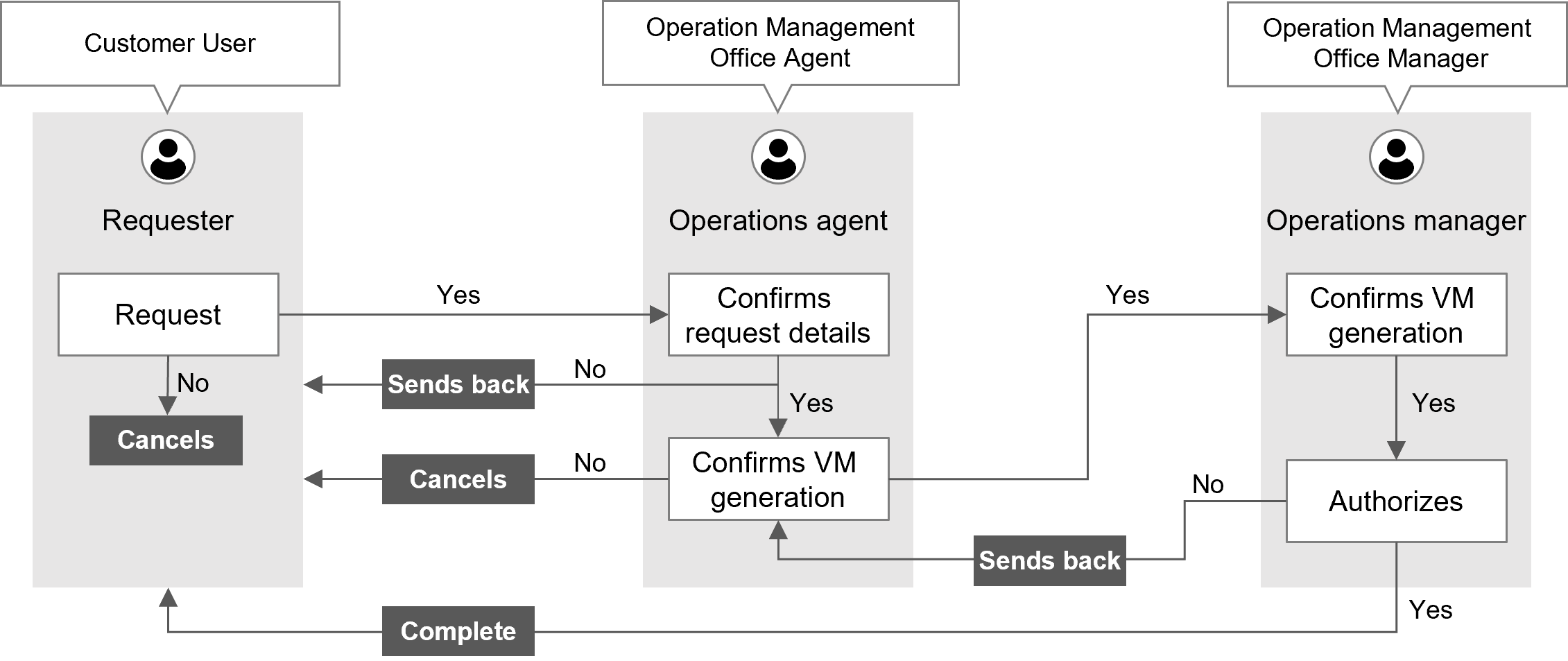
Using VM lending as an example, the required roles are listed below. The appropriate role must be assigned to each step.
(Figure) Workflow with VM lending as an example
(Table) List of roles with VM lending as an example
| Work task name | Workflow step | Operator | Pre-Installed role |
|---|---|---|---|
| VM lending | |||
| Makes a request | Requester | Customer User | |
| Reviews the request | Operations agent | Operation Management Office Agent | |
| Creates a VM | (Automatic execution) | - | |
| Confirms VM generation | Operations agent | Operation Management Office Agent | |
| Approve | Operation manager | Operation Management Office Manager | |
The Pre-Installed and Primitive roles are predefined in Ops I as standard roles. For details on standard roles, see “Correspondence between roles and support functions in Ops I”.
Also, be sure to set the Pre-Installed role “Customer Manager” or “Customer User” for customer users.
The “Customer User” is assigned the Primitive role “customer” and can be restricted to operate only on records related to the customers to which it belongs.
If the standard roles provided by default do not accommodate your needs, you can create any custom ACL and apply it to your custom roles. If you wish to change the permissions of a standard role, you can do so by assigning a custom ACL to the custom role that describes the Pre-Installed role and the differing permission information.
For details, see “API reference overview” > “Details of API function and execution examples” > “Assigning custom ACLs to roles and removing custom ACLs assigned to roles” > “Assigning ACLs to roles” in “JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration API Reference”.
By specifying the Statement in the YAML definition of the ACL, you can define permission information, such as the access control to resources required for each user.
The Pre-Installed role “System Security Administrator” must be configured in order to register, update, and delete ACLs and Statements.
 Notes
Notes
- The standard ACLs provided by default cannot be assigned to custom roles.
- Do not change ACLs assigned to the standard roles.
[ACL]
An ACL is a list of permissions that grants users, groups, and roles access to the resources they need, controlling user access to URIs, documents, UI components, data objects, and more.
There are three authorization types for ACLs.
- URI authorization
You can set authorization conditions for URIs in Ops I for applicants.
The URI used in Ops I can be specified for the target resource. - Document authorization
You can specify authorization conditions for Ops I YAML files to the applicant.
You can specify a key-value for the target resource that is allowed for the YAML file the user receives. - Object authorization
You can specify authorization conditions for data input/output of the Ops I API to the applicant.
You can specify the conditions of records that users can input and output to the target resource.
See the API Reference for supported APIs.
[Statement]
Statement is a set of permission information in the YAML definition of an ACL.
The YAML definition of the Statement defines the access to the resource and the permission information for the operation to be performed.
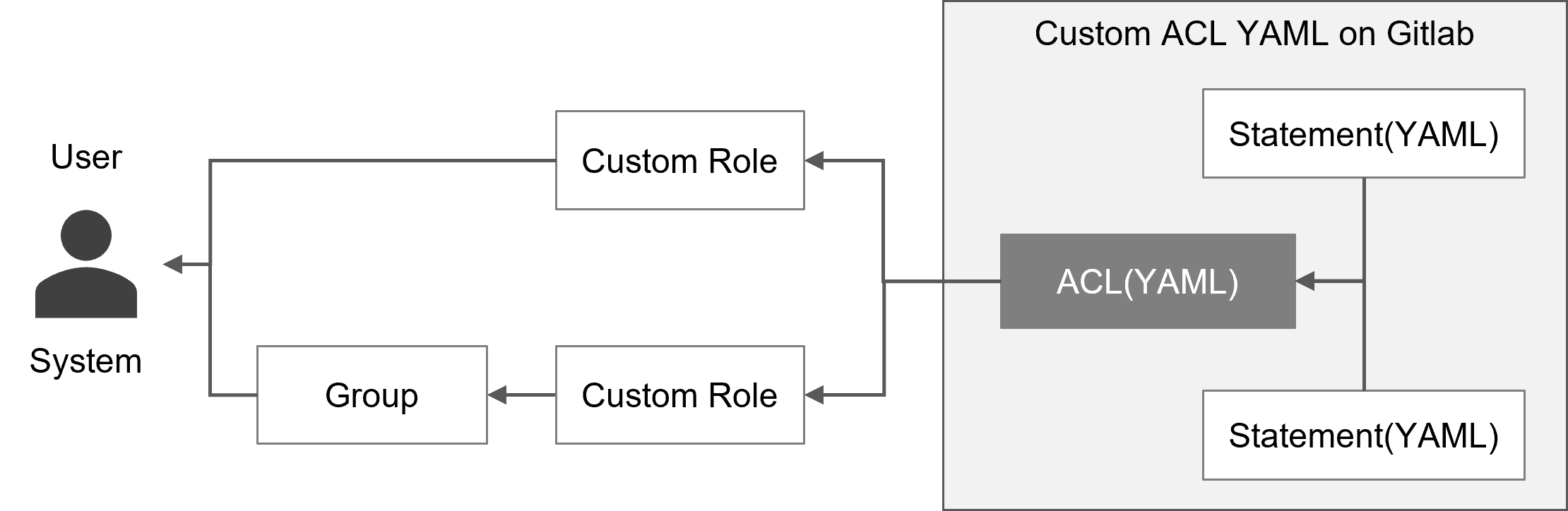
(Figure) How to apply custom ACL
(Table) Items required to apply a custom ACL
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom role | Roles can be created for custom ACLs. Custom ACLs can be assigned to users and groups in a flexible manner by allowing a limited set of permissions to be assigned. |
| Group | Custom roles with custom ACLs can be assigned to groups to grant permissions only to a specific group. (e.g., projects, not divisions) |
GitRole also allows controlling access to the repository (documents) for users assigned to the group.
For details on YAML definitions of ACLs, see “ACL, Statement”.