4.10 Extending the environment for automatic execution
In order to achieve automation using additional modules including the Ansible collections and Python modules, or additional tools including the AWS CLI and OpenTofu, the execution environment provided by Ops I must be extended. A user-extended execution environment is referred to here as a custom execution environment.
The execution environment is created and managed by the Git application (GitLab). In addition, the automation is executed by the automation application (AWX). For information on the GitLab and AWX manuals, see “OSS version/edition and reference manuals”.
The flow of extending the automated execution environment is as follow.
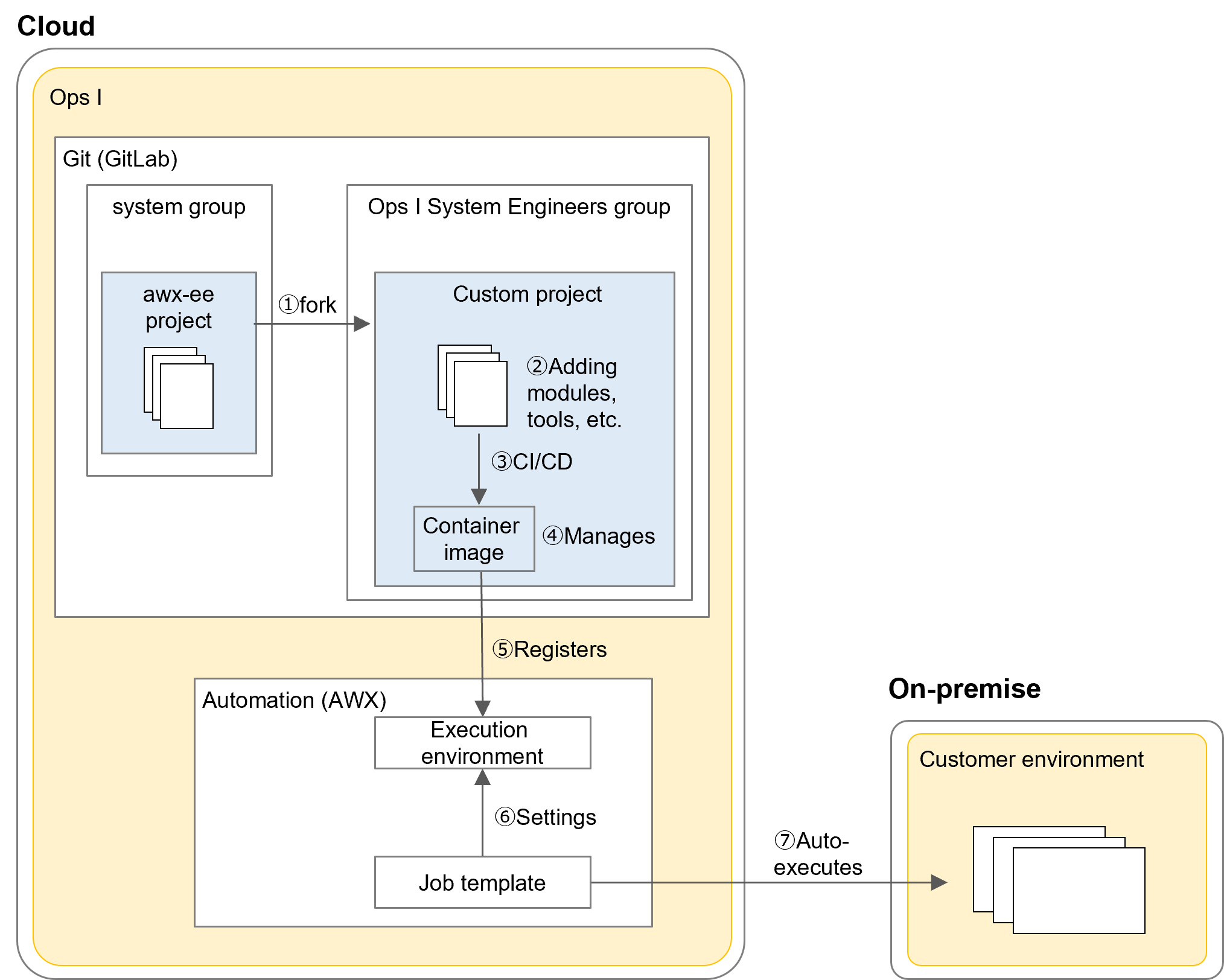
(Figure) Flow of extending the automated execution environment
The flow of extending the automated execution environment and executing automation is as follows.
- Developing custom execution environments: ①, ②, ③
- Managing custom execution environments: ④
- Registering custom execution environments with AWX: ⑤
- Executing automation: ⑥, ⑦
Users responsible for “Developing custom execution environments”, “Managing custom execution environments”, and “Registering custom execution environments with AWX” must be assigned the Pre-Installed role “Site Reliability Engineer”.
Users responsible for “Executing automation” must be assigned the Pre-Installed role “Operation Management Office Agent”.
For details on roles, see “Correspondence between roles and support functions in Ops I”.
Users responsible for addition of execution environments must be assigned the “Execution Environment Administrator” and “Administrator” roles within the organization. For information on roles within organizations, see “Organization management”.
In addition, to fork a GitLab project, you must have a Git role of “Maintainer” or higher for the GitLab group “ops-i-system-engineers”. For information about Git roles, see “(Table) Related resources area tabs when adding a group”.
Details of each task are as follows.
(1) Developing custom execution environments
Develop the custom execution environment. Perform the tasks in this section in the Git application.
- In the GitLab GUI, select the [awx-ee] project in the [system] group. [awx-ee] is a read-only project.
- Click the [fork] button. When the window for selecting the forking destination opens, select [ops-i-system-engineers]. Enter the following items and click the [Fork project] button to create a custom project.
(Table) Items to enter to register custom projects
Item Description Project name Arbitrary value Project slug Arbitrary value
However, the following reserved words should not be used.- GitLab reserved words. For the reserved words, see the following.
"Reserved project names" in https://archives.docs.gitlab.com/17.3/ee/user/reserved_names.html - Values beginning with "opsi"
Visibility level Select [Private] - GitLab reserved words. For the reserved words, see the following.
-
Select [Setting] - [General] for the forked project and click the [Expand] button under [Visibility, project features, permissions]. Enable the following items that appear.
- CI/CD
- Container registry
- In the following files of the custom project, add information on the modules and tools to be included in automation.
(Table) Editable files of custom projects
The following files do not need to be changed.File Description _build/requirements.yml List of ansible collections and roles to be installed
Described in the ansible requirements file format._build/requirements.txt List of Python packages to be installed.
Described in the pip requirements file format._build/bindep.txt List of rpm packages to be installed.
Described in the bindep requirements file format._build/additional_script bash script to run the above three files after installation.
Users can install tools such as AWS CLI and OpenTofu.
(Table) Files of custom projects that do not need to be changed
For available Ansible collections, Ansible Core versions, and Python versions, see "OSS version/edition and reference manuals".File Description Dockerfile Describes the image of the execution environment for Linux. The base image is quay.io/ansible/awx-ee, Ops I's built-in execution environment. Refers to a configuration file for customization. .gitlab-ci.yml Builds the Dockerfile and pushes the image of the custom execution environment to the Container Registry.
- Select [Repository] - [Tags] to set a tag for the custom project. Any string can be used for the tag name. The tag must be set for the main branch.
Setting the tag automatically triggers build of the custom execution environment image. The created image is automatically pushed to the [Container Registry] of the custom project.
The image is named according to the following rule.
registry.Ops I Domain/ops-i-system-engineer/Project Name:Tag Name
 Notes
Notes
The CI/CD pipeline execution times out after one hour and fails to build the container image.
(2) Managing custom execution environments
Manage the custom execution environment image created in “Developing custom execution environments”. This operation is required for referring to created images and deleting unnecessary images. Perform the tasks in this section in the Git application.
 Notes
Notes
Set the image when registering an AWX execution environment in "Registering custom execution environments with AWX". Confirm that a tag of an image to be deleted is not set for the execution environment already registered with AWX by using, for example, the search function on the execution environment list window.
The procedure for managing the image is as follows.
- Open [Packages and registries] - [Container Registry] for the custom project to display the image developed in "Developing custom execution environments".
- Select [Settings] - [Packages and registries] - [Set cleanup rules] for the custom project and check [Enabled] to enable execution of the Cleanup Policies. This causes tags to be periodically removed according to the specified Cleanup Policies. For details, see the GitLab manual.
https://archives.docs.gitlab.com/17.3/ee/user/packages/container_registry/reduce_container_registry_storage.html#cleanup-policy
As a result, the tag set in "Developing custom execution environments" will be deleted.
(3) Registering custom execution environments with AWX
Register authentication information for AWX to access the custom execution environment (image) in GitLab and register the custom execution environment with AWX. Perform the tasks in this section in the Git application and automation application.
- Obtain the GitLab access token.
For details, see "Obtaining GitLab access tokens". However, when obtaining a GitLab access token, "Select scopes" should check "read_registry". - Register the GitLab access token in the HashiCorp Vault secret.
For details, see "Creating a secret". - Register authentication information to access the custom execution environment. For details on registering authentication information, see "Registering authentication information". Details of the setting items are as follows.
(Table) Authentication information to access the custom execution environmentItem Description Name Arbitrary value Authentication Information Type Container registry Authentication URL registry.Tenant Name.ops-integration.com User Name User Name from which you obtained the GitLab access token in Step 1 Password or Token GitLab access token obtained in Step 1 - Register the custom execution environment with AWX. In the automation application, click the [Admin] - [Execution Environment] - [Add] button. Set the following items and click the [Save] button.
(Table) Registering the custom execution environmentItem Description Name Arbitrary name Image URL of the image displayed in Step 1 of "Managing custom execution environments".
Set the tagged URL copied from the [Container Registry] window.
Example: registry.Tenant Name.ops-integration.com/ops-i-system-engineer/Project Name/Tag NamePull Select [Always pull before execution] or [Pull only when the image does not exist]. Registry authentication information Authentication information for AWX access created in Step 3
(4) Executing automation
Perform the tasks in this section in the automation application.
- Configure the custom execution environment registered in "Registering custom execution environments with AWX" when registering a job template for automation. For information on registering job templates, see "Registering templates".
- Execute the job template. At this time, automation is executed according to the settings of the custom execution environment.
Job templates can be executed from a workflow, for example. See "Setting up automatic job execution".