4.9.2.2 Registering incidents
This function allows events managed in JP1/IM to be registered as Ops I tickets.
This allows status management and ticket handling to be performed in Ops I.
(1) Prerequisites
The JP1/IM addresses must be added as permitted inbound IP addresses in Ops I.
Users who configure the settings must meet the following conditions.
- The Ops I Primitive role “user_admin” is assigned (for issuing Ops I tokens).
- The Ops I Primitive role “itsm_viewer” is not assigned (for creating tickets).
For details on the Ops I roles, see “OPS I Roles”.
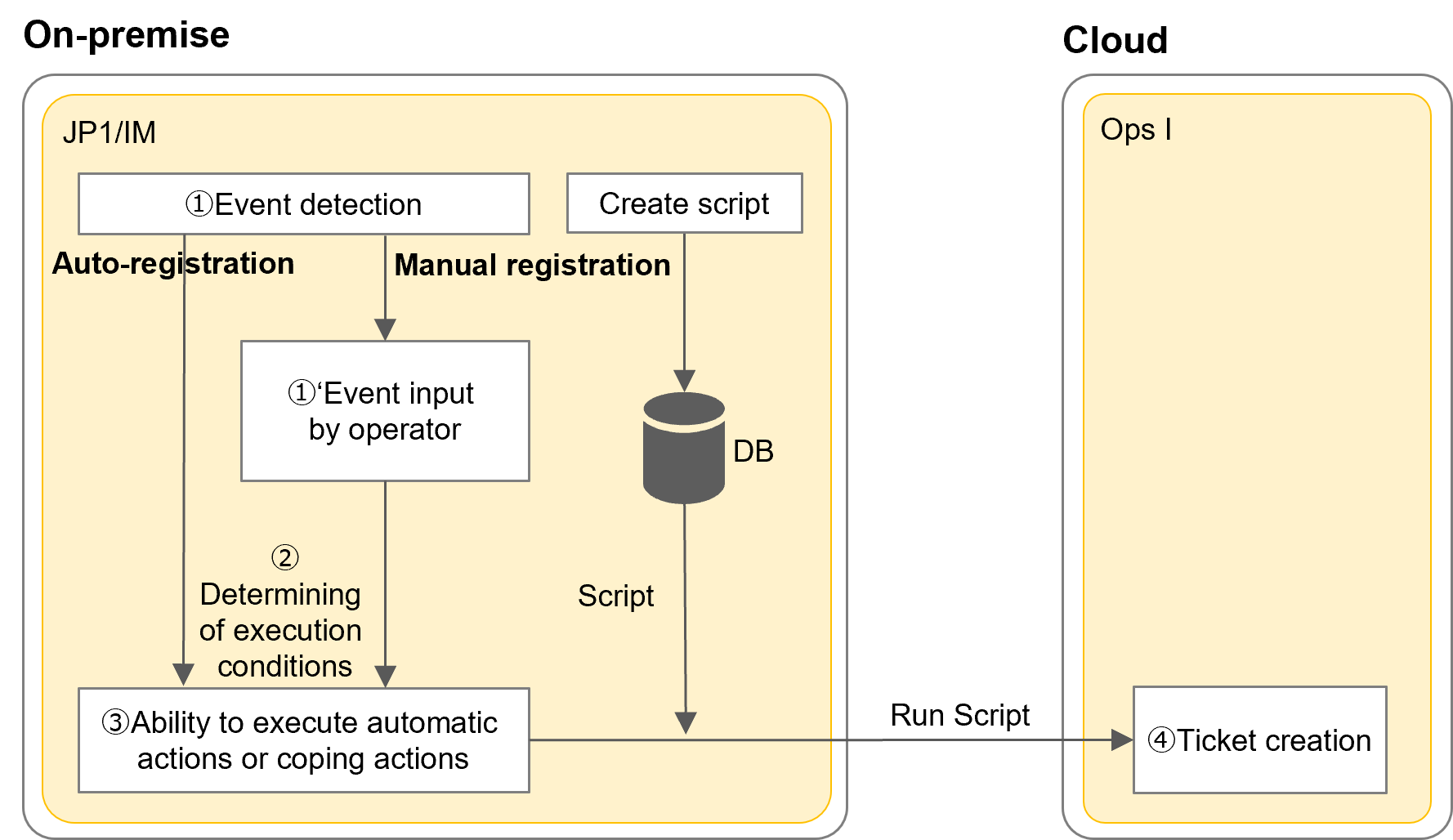
(2) Flow of registering incidents
The flow of registering incidents is as follows. Use the JP1/IM automatic action and coping action functions to register incidents. There are two type of coping action functions: automatic and manual execution.
The execution process varies depending on the registration method.
- Automatic registration: automatic action function, coping action function (automatic execution)
- Manual registration: Coping action function (manual execution)
(Figure) Flow of incident registration
The flow of registering incidents is as follows.
(3) Settings for registering incidents
The settings required for incident registration using the JP1/IM linkage templates are as follows.
- Proxy
- Ops I token
For details, see "API reference overview" > "Prerequisite knowledge" > "Obtaining Ops I tokens" in "JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration API Reference". - Ops I URL information
- Ticket registration information (optional)
An example script file is shown below.
echo off
setlocal
REM First command line argument is EVID, Second is EVSEV, Third is EVDATE, Fourth is EVTIME, Fifth is EVHOST, Sixth is EVPID, Seventh is EVSEQNO
set TITLE=Event ID (Basic Code:Extended Code): %1, Severity: %2
set DESCRIPTION=Time of Occurrence: %3 %4^^^<br^^^>Issuer Hostname: %5^^^<br^^^>Issuer Process ID: %6^^^<br^^^>Serial Number in Issuer Event DB: %7
curl -XPOST "https://Ops I URL
/capi/v1/tickets" ^
-H "accept: application/json" ^
-H "Content-Type: application/json" ^
-H "X-OpsI-Token: Ops I Token
" ^
-d "{¥"title¥": ¥"%TITLE%¥", ¥"description¥": ¥"%DESCRIPTION%¥", ¥"type¥": ¥"incident¥"}"
endlocal
The JP1/IM attributes used in the script file are as follows.
| Variable | Event information to be communicated |
|---|---|
| EVID | Value of event ID converted to the format of "Basic Code:Extended Code".
|
| EVSEV | Event extended information severity (Emergency, Alert, Critical, Error, Warning, Notice, Information, Debug): Value of severity (E.SEVERITY) |
| EVDATE | Value of event registration time (B.TIME) converted to the format of "yyyy/mm/dd". |
| EVTIME | Value of event registration time (B.TIME) converted to the format of "hh:mm:ss". |
| EVHOST | Event issuer hostname: Value of issuer event server name (B.SOURCESERVER) |
| EVPID | Value of event issuer process ID (B.PROCESSID): Process ID of the issuing application program |
| EVSEQNO | Value of serial number in event DB (B.SEQNO) |
For automatic actions
Path to the Script¥Script File Name.bat $EVID $EVSEV $EVDATE $EVTIME $EVHOST $EVPID $EVSEQNO
For coping actions
Path to the Script¥Script File Name.bat ${event:EVID:} ${event:EVSEV:} ${event:EVDATE:} ${event:EVTIME:} ${event:EVHOST:} ${event:EVPID:} ${event:EVSEQNO:}
When registering incident tickets in Ops I with automatic actions or coping actions (auto execution), limit the number of times of action execution to avoid performance degradation. For that, limit the number of events that execute automatic actions using the setting to suppress the same action or the common exclusion conditions, or specify the conditions to execute the action in the action definition.
For details, see the sections on configuring automatic and coping actions in the JP1/IM manual "Overview and System Design Guide".
(4) Reflecting to tickets
Tickets are created as follows. The user associated with the Ops I token will be the creator of the ticket.
The Criticality, Impact, Priority, Category and Queue are filled in with default values, so change them as appropriate.
(Table) Fields of tickets to be created
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Set to "incident". |
| Criticality | Defaults to "medium". |
| Impact | Defaults to "medium". |
| Priority | Defaults to "medium". |
| Category | Defaults to "unclassified". |
| Queue | Defaults to "Raw". |
| Title* | Set to the following event information.
|
| Description* | Set to the following event information.
|