4.4 UI design
UI design involves definitions in the UI and Script YAML files.
UI YAML files are available for UI versions 1.0 and 1.1 and it is recommended that you use UI version 1.1 when creating a new UI. For details on the UI versions, see “UI version”. For information on the function to define UI URLs (Uipath), see “Defining window URL (Uipath)”.
Some scripts are written in JavaScript. For details, see “Script”.
(Table) UI design items and outline
| Item | Definition method | Key design points |
|---|---|---|
| UI | ・YAML file | Identify what are needed on the window, such as the types of operation buttons and input items, and consider the window configuration in advance, including how to arrange the items. |
| Script | ・YAML file ・JavaScript |
Definitions of actions to execute when menus or other items on the UI are operated can be customized, but consider consistency across operations, for example, by utilizing built-in Ops I components. |
[UI definitions]
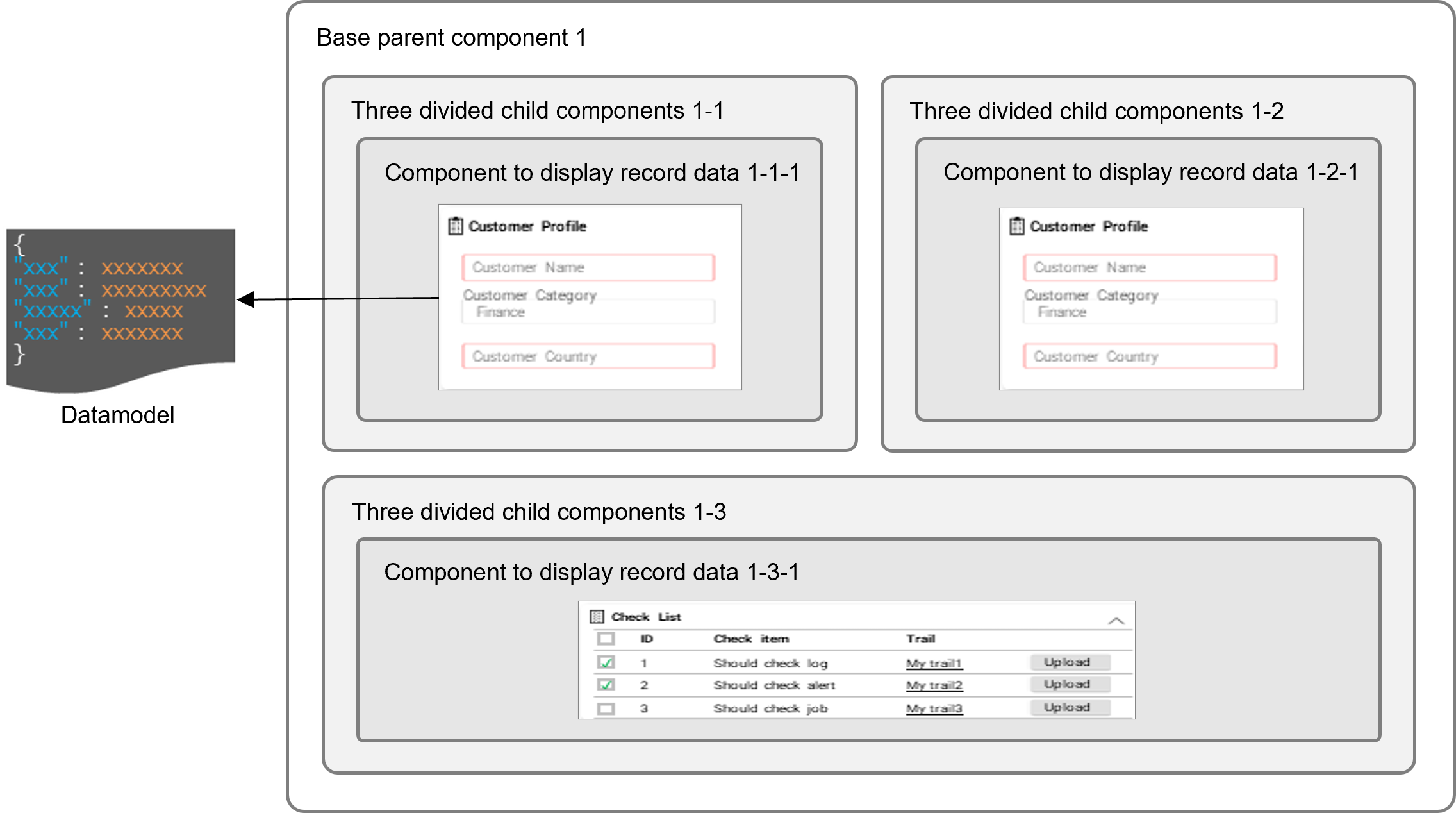
UI definitions define the window used in each step of the workflow. Compose a window by arranging components representing various UI parts to display. In addition to components, configure buttons and menus to perform actions.
In Ops I, windows are composed by combining multiple components. For records and lists displayed in windows, use data defined in data models.
For details on data models, see “Designing a data model”, “Datamodel”.
When saving attachments on Form components of UI version 1.0, use the Ops I-provided action buttons such as “save” and “accept” to perform the saving operation. UI version 1.1 allows the use of custom scripts.
(Figure) Component combinations conceptual diagram
[Script]
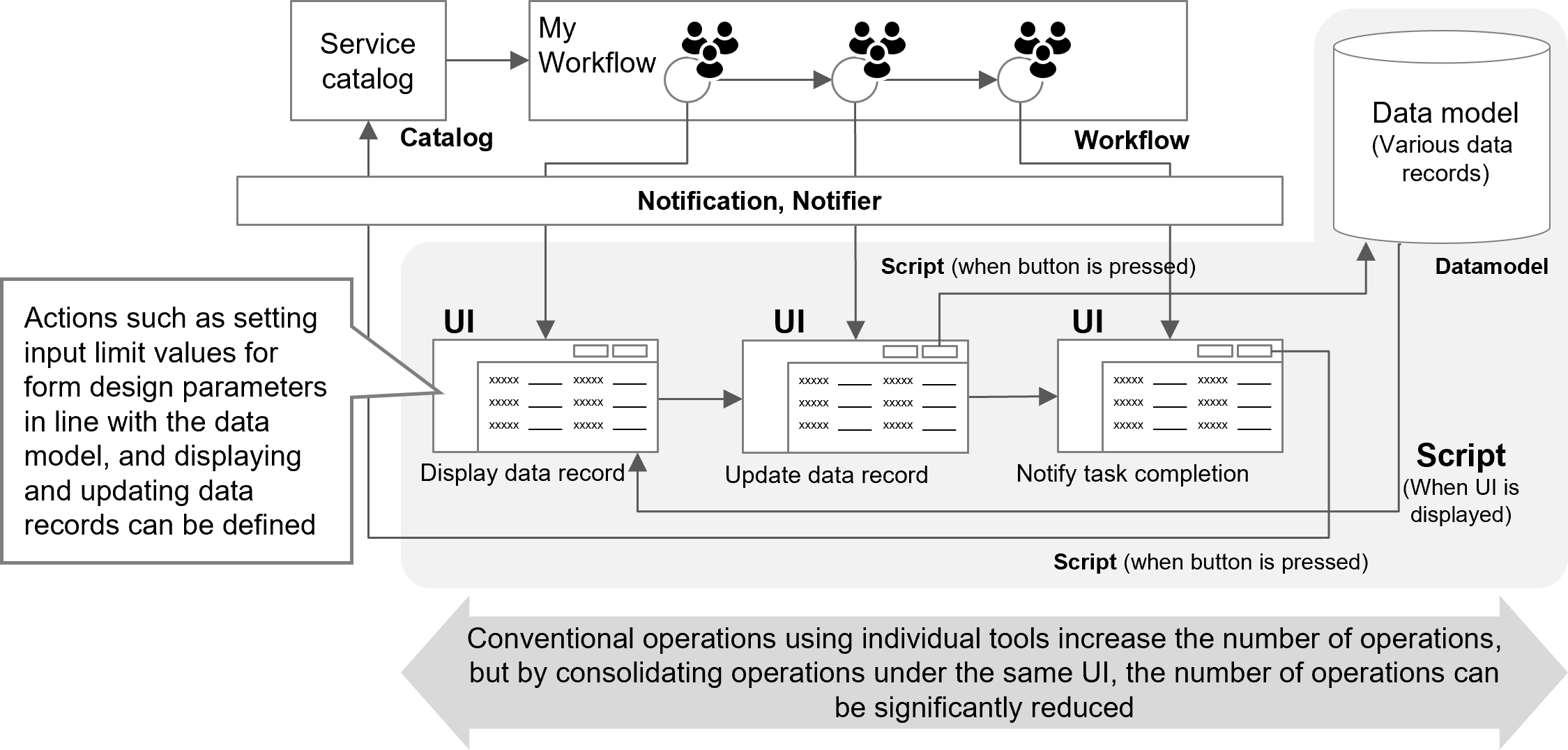
In the Script YAML file, you can define actions (behaviors) for components such as items and buttons to be placed on the windows defined in the UI YAML file.
Simple actions such as validation checks performed when certain fields are filled in can be implemented by using YAML definitions only while more advanced checks and actions can be implemented by using scripts.
For example, to require Item B to be entered if Item A is entered when the button is clicked, a script can be used to check the correlation between the input values. It is also possible to automatically calculate the sum of the input values A, B, and C and populate certain items, or to reflect the input values in a different data model.
(Figure) UI and script outline chart
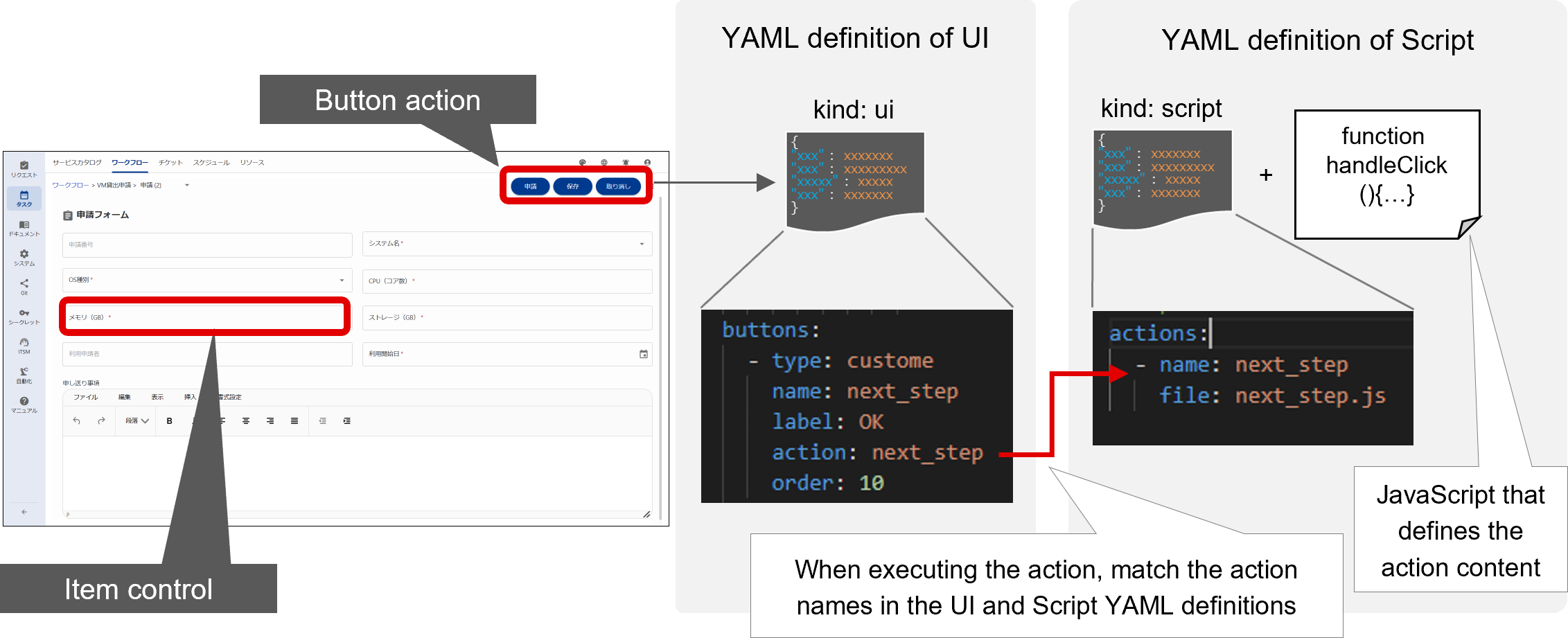
An action defined in the Script YAML file is executed when it matches the name of the action for the component defined in the UI YAML file. Therefore, definitions in the Script and UI YAML files should be created taking correspondence into account. The following is a conceptual diagram of a Script and what to define in the YAML file.
For details on Script YAML definitions, see “Script”.
(Figure) Script conceptual diagram
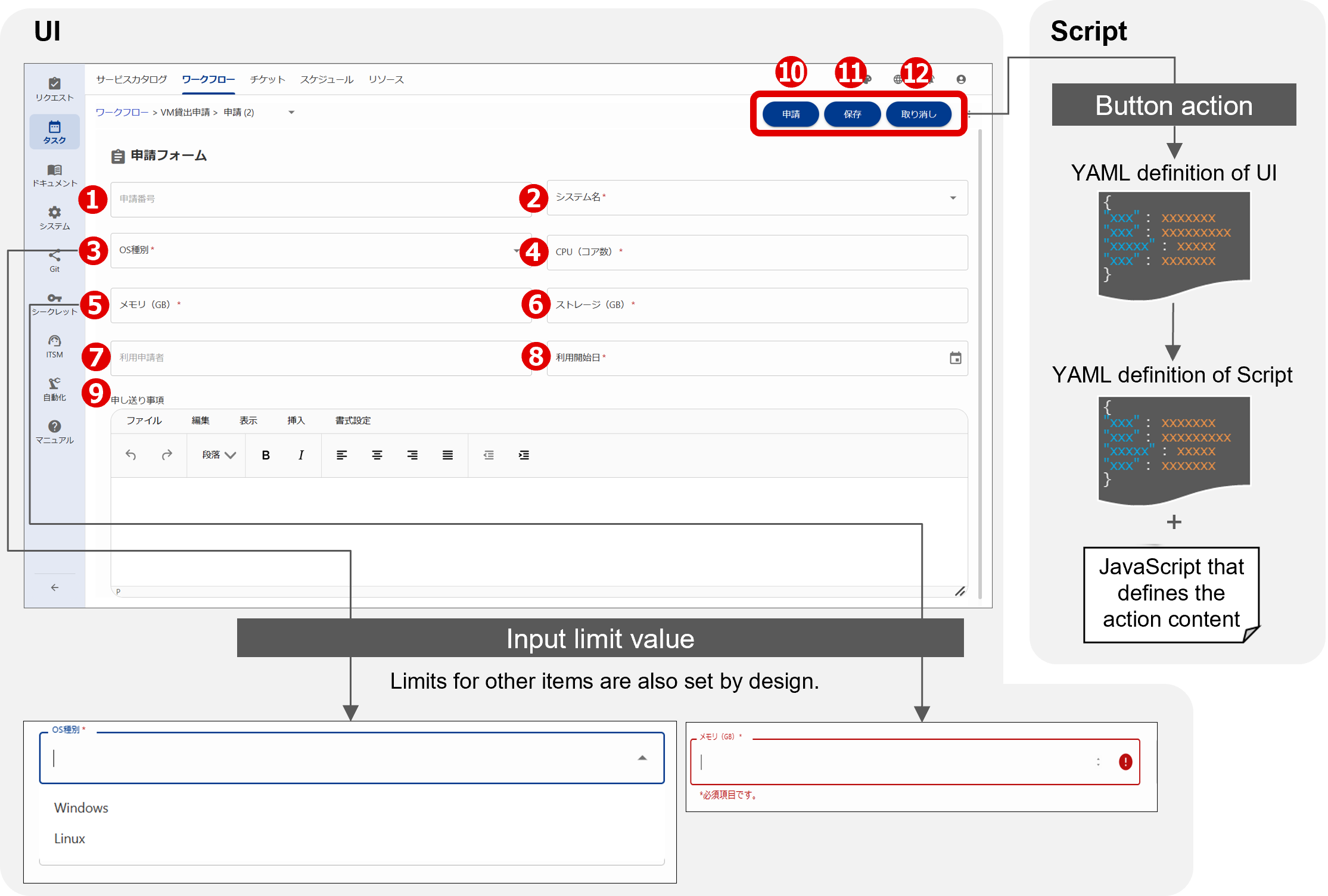
For example, for VM lending requests, consider how to display each item such as the application number based on how it is to be operated in the window, and define the type of parameters and buttons in the UI YAML file accordingly. Below are a list of settings and a figure of a window configuration example in the case of VM lending.
(Table) List of settings using “Request” for VM lending as an example
| Task name | work flow Step |
Operator | UI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Name | Action | Performing validation check |
Note | ||||
| VM lending | Makes a request | Requester | Parameter | Request number | ❶ | Display only | - | Auto-numbered |
| Parameter | System name | ❷ | Waiting for input (required) | - | Selected from list | |||
| Parameter | OS type | ❸ | Waiting for input (required) | - | Selected from list | |||
| Parameter | CPU | ❹ | Waiting for input (required) | 4≦Value≦128 | Message is displayed when there is a check error | |||
| Parameter | Memory | ❺ | Waiting for input (required) | 32GB≦Value≦256GB | Message is displayed when there is a check error | |||
| Parameter | Storage | ❻ | Waiting for input (required) | 10GB≦Value≦4,096GB | Message is displayed when there is a check error | |||
| Parameter | Requester | ❼ | - | - | - | |||
| Parameter | Use start date | ❽ | Waiting for input (required) | - | - | |||
| Note | Messages | ❾ | Waiting for input (optional) | - | - | |||
| Button | Make a request | ❿ | Submit the request | - | - | |||
| Button | Save | ⓫ | Save the request | - | - | |||
| Button | Cancel | ⓬ | Cancel the request | - | End the workflow | |||
The numbers circled in red in the table and in the figure below indicate how the settings are used to configure the window.
(Figure) Image of the window configuration using “Request” for VM lending as an example
■ ClientScript
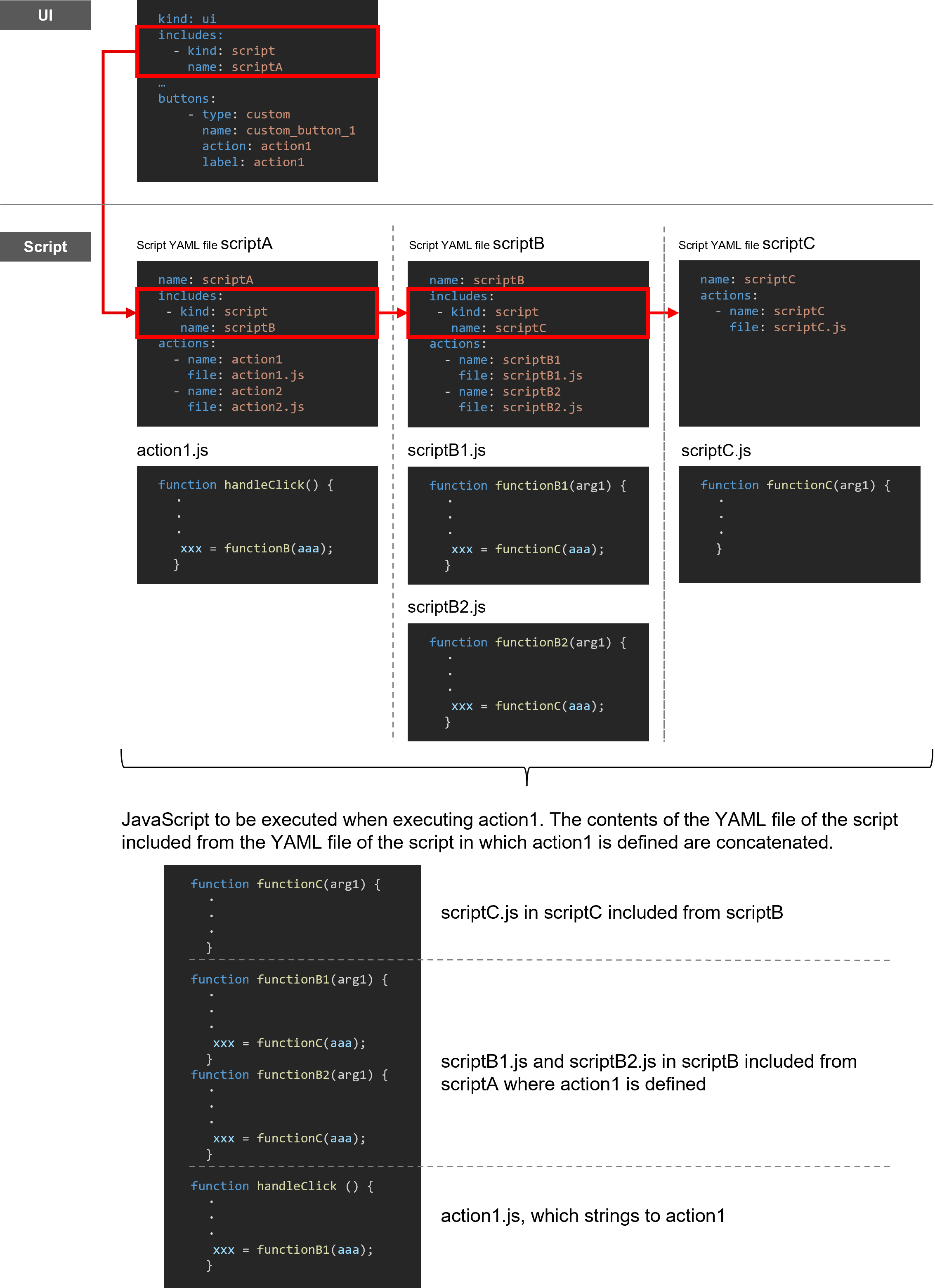
By specifying a Script YAML file as an Include target in another Script YAML file, the JavaScript file defined for the action for the Include target can be called and executed. This allows multiple JavaScript files to be executed for a single action in the Include source.
(Figure) Example of using Include in Script YAML definitions
As shown in the figure above, even if Includes are hierarchical, the JavaScript file defined for actions for all levels can be called and executed.
Ensure that actions for Include targets refer to JavaScript library files rather than certain button actions. If JavaScript files defining functions, etc. are prepared in advance, you can define multiple actions just by specifying the files as Include targets.
 Notes
Notes
- When registering YAML files with dependencies for Include in GitLab, register the YAML file to be included first. If the YAML file to be included does not exist in the registration destination, the other YAML file cannot be registered.
- When registering the Include source and target files at the same time, there is no need to be aware of the order of registration.
- YAML files cannot be Included in each other.
- When a Script YAML file is Included in another Script YAML file, the JavaScript files specified in the Include target and source will be combined and executed. For this reason, there is no need to make import or export declarations in JavaScript.
In the Include target, do not define functions (function), classes (class), constants (const), variables (let), or global-scope variables (var) with the same name as the Include source. Otherwise, variables/functions defined in one file may be overridden by variables/functions defined in the other file, or the script may terminate abnormally during execution. - Name user-defined functions, classes, constants, and variables like "<Script_YAML_Definition_Name><Filename_without_Extension><Function_Name>" to avoid name conflicts between JavaScripts.
- Do not define classes, functions, variables, or constants beginning with "OI".
- Do not override methods or properties in classes beginning with "OI".
Section structure
4.4.1 UI version
4.4.2 Defining window URL (Uipath)
4.4.3 Saving a table display
4.4.4 Displaying hint messages