1. Overview
The Ops I ITSM application provides a variety of customer and ticket-related functions in conjunction with OTOBO.
This document describes the functionality of OTOBO, which is supported as an ITSM application for Ops I, by use case (Chapter 2) and by function (Chapters 3-9). In addition, tickets and roles that are operated or set up outside of the ITSM application are expressed with “Ops I”. (Example: Ops I ticket)
Before performing each operation, please check “Prerequisite knowledge” and “Preparation” and perform the necessary work.
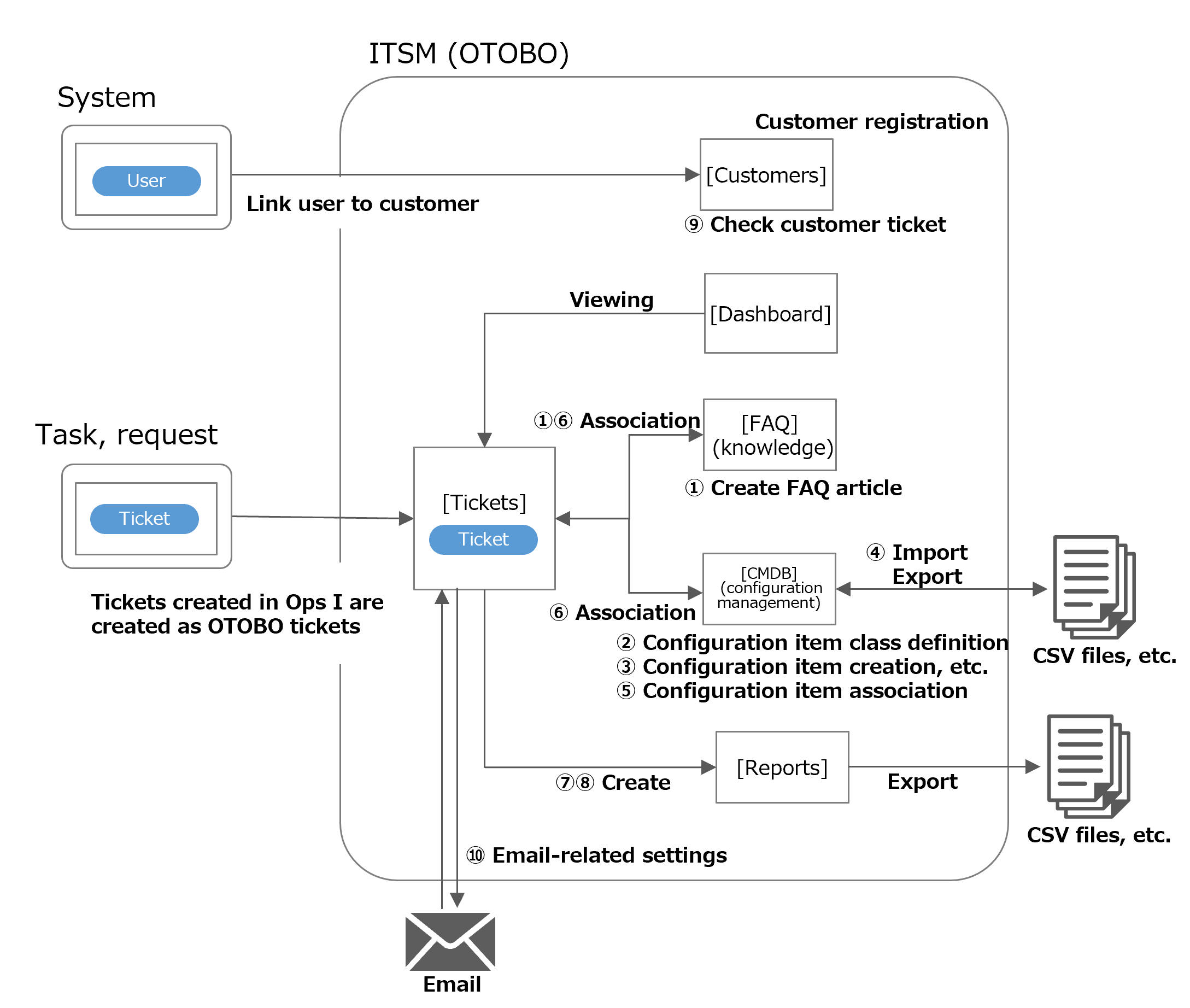
The following figure illustrates the positioning of ITSM applications within Ops I. The use cases described in this document are listed in ① through ⑩, and each function is enclosed in [].
(Figure) ITSM application functions
For details on use cases ① through ⑩, see the table below. For details on supported functions, see “Supported functions”.
| Use case | Refer to | |
|---|---|---|
| ① |
|
Use cases for FAQ articles (knowledge) |
| ② |
|
Define configuration item classes and managed items |
| ③ |
|
Create, browse, update, and delete configuration items |
| ④ |
|
Update by exporting and importing a list of configuration items |
| ⑤ |
|
Associations between configuration items |
| ⑥ |
|
Use cases for incident management |
| ⑦ |
|
Ticket list statistics |
| ⑧ |
|
Aggregate statistics |
| ⑨ |
|
Use cases for customer management |
| ⑩ |
|
Use cases for notifications and email-based ticket creation |
The functions that can be used in conjunction with other applications are described below.
[Customer-related]
The system application creates users and configures customer users. Among the users created, customer users and OTOBO personnel (users who have been granted the necessary roles and access to the ITSM application) are automatically registered as OTOBO users.
With the ITSM application, you can register customers and check tickets by customer.
For details on defining customer users and OTOBO personnel, see “Log in/log out”. For details on creating users and linking users to customers, see “Functions > System > User management” in “JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User’s Guide”.
[Ticket-related]
The Tickets function of the Task and Request applications allows users to create, edit, and view tickets. Tickets are automatically created as OTOBO tickets.
The ITSM application allows for smoother operation and management of tickets, including incident response, by viewing tickets, linking to FAQ articles (knowledge) and configuration items, and aggregating the number of tickets and other information.
For details on operations in the Task and Request applications, see “Functions > Tasks and Requests > Tickets”, “Designing and Building Your Operation > Task design > Ticket management”, and “Designing and Building Your Operation > Other operational design tips > Customizing the ticket window” in “JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User’s Guide”.
Chapter structure
1.1 Supported functions
1.2 Prerequisite knowledge
1.3 Preparation
1.4 Temporary restrictions