6. YAML Definition
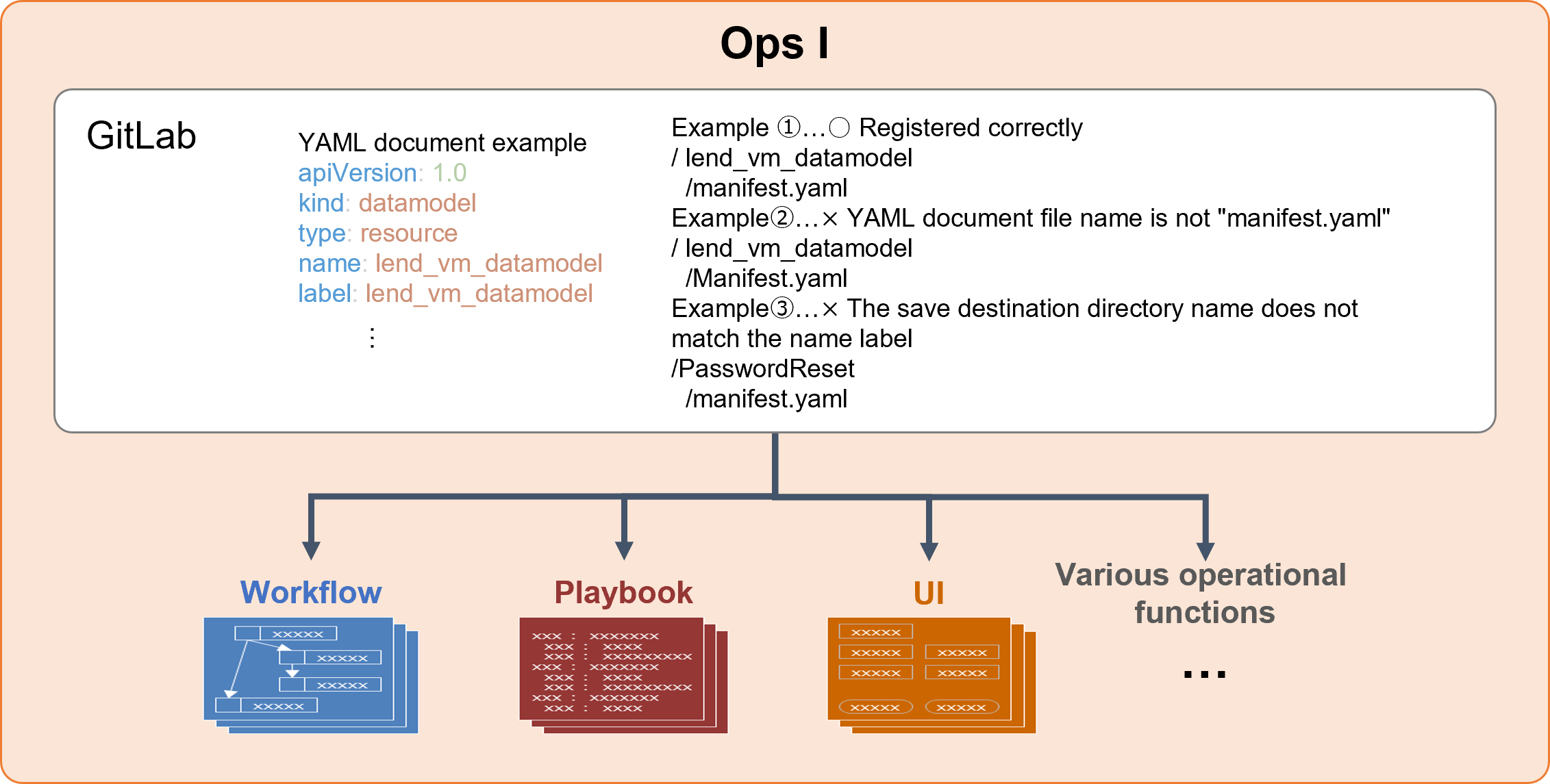
Ops I allows you to add definitions required for operations, such as workflows and datamodels, in YAML files, making it possible to realize Operations as Code (OC). Registering coded operations with Ops I automatically converts them to their respective operational functions.
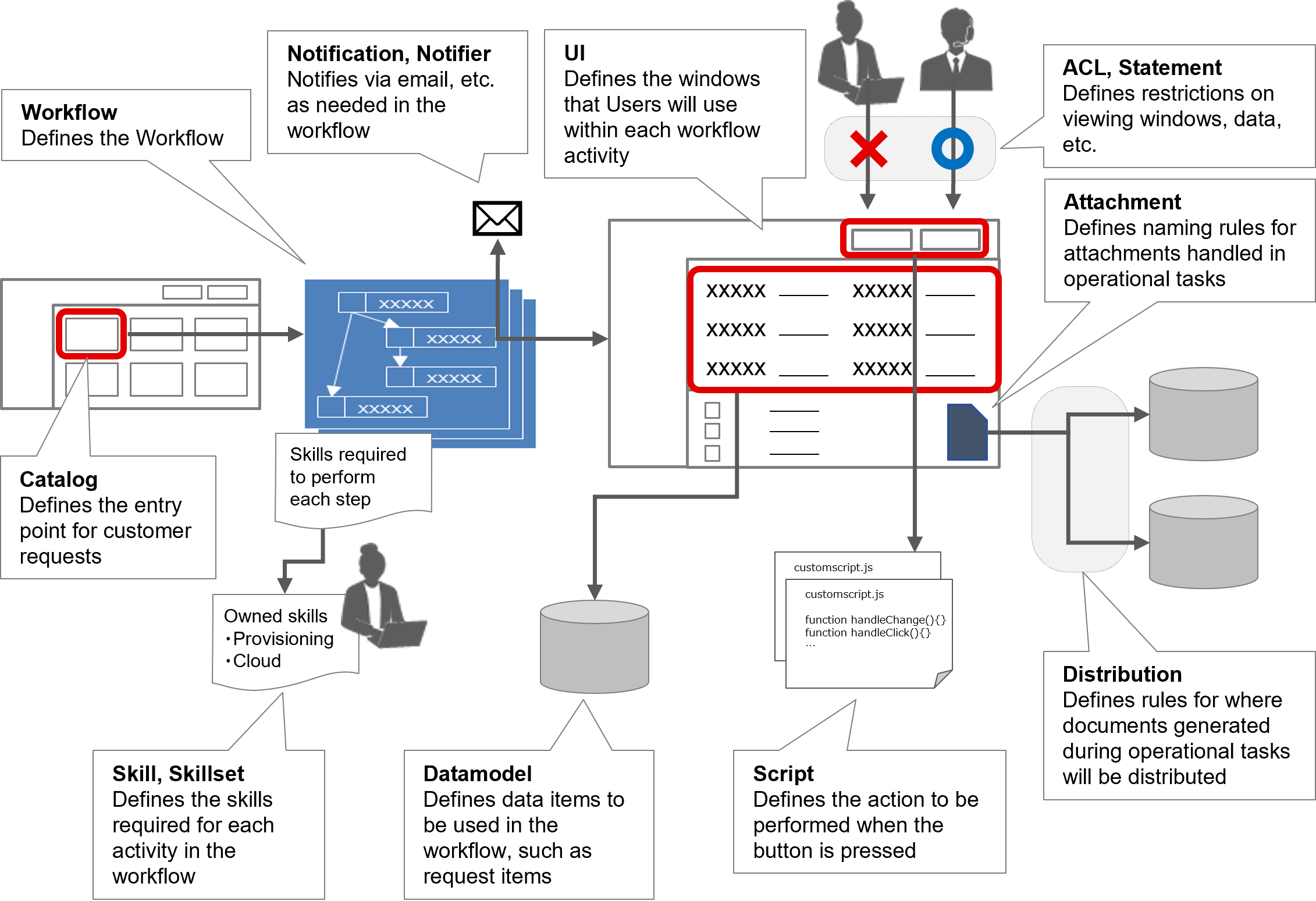
A list of operational functions that can be added in YAML files is provided below.
(Figure) Relationship between YAML files and operational functions
(Table) Operational functions that can be added in YAML files
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Workflow | Define workflows required for operation. |
| UI | Define the UI, including data to be displayed and window layout. |
| Datamodel | Define a datamodel for storing various types of data. |
| Catalog | Define the service catalog, which is where users make various types of applications. |
| Script | Define actions that are triggered by a particular event, such as when a certain window is displayed or a button is clicked. |
| Attachment | Define naming rules for attachments to be handled during operations. |
| Distribution | Define the rules by which the various types of documents are generated during operations and where those documents should be saved. |
| ACL | Define which users and groups will be authorized as defined in the Statement. |
| Statement | Define authorization settings for various resources, such as URI and table records. |
| Notification | Define who to notify and what to notify when there is an event on Ops I. |
| Notifier | Define the method by which the contents of the notification defined in Notification are delivered. |
| Skill | Define how to visualize the experiences, qualifications, and other skills that each user possesses. |
| Skillset | Define a set of skills required to execute each step in a workflow. |
If coding operational functions in Ops I, it is necessary to write YAML files following a specified format. Detailed descriptions of YAML files for each of the operational functions are provided in “Workflow” through “Calendar”.
[Notes on creating YAML files]
- The YAML file name must be "manifest.yaml".
- You must save the YAML file under a directory with the same name as specified in the top-level "name" label.
- The combination of the "kind" label and the "name" label must be unique in Ops I.
- To avoid conflicts with reserved words, you must add a prefix to the YAML file "name" label and the datamodel table name. If a conflict with a reserved word occurs, an error will result. For details, see "Actions to take when a YAML file cannot be registered due to an error with the "name" label or datamodel table name".
- If the "name" label in an included YAML file conflicts with another "name" label, unintended behavior will occur. For details, see "Actions to take when no error message appears but unintended behaviors occur".
YAML files can be loaded from Ops I by registering them in a repository within a user-defined group. As a result, Ops I automatically generates the corresponding operations functions. For information on how to register YAML files, see “Register YAML files with GitLab (GUI)” and “Register YAML files with GitLab (CUI)”.
(Figure) How to register YAML files
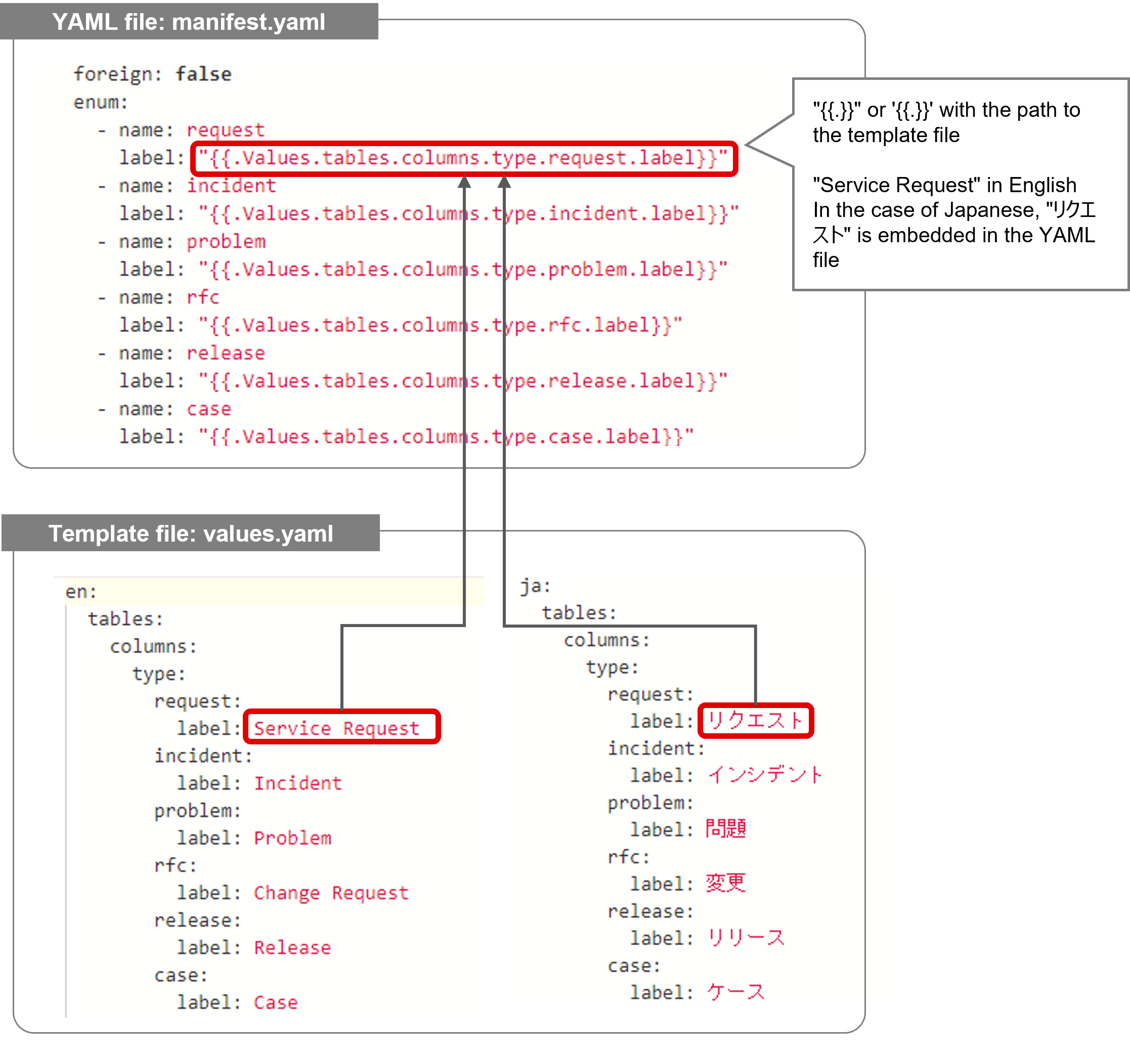
The template function can also be used to define YAML files.
The template function is a document function that enables terms defined as environmental parameters in YAML files to be replaced with user-defined or system-defined parameters. This is useful for supporting multiple languages, etc.
[User-defined parameters]
“YAML files” that use the template function and “template files” that contain reference values must meet the following conditions.
- The YAML file and template file must be placed in the same folder.
- The name of the template file must be “values.yaml”.
- The chapter structure used in the YAML file must be the following format.
"{{.Values.the path specified in the template file}}"
'{{.Values.the path specified in the template file}}'
<YAML files that can use parameters>
- application
- ui
- library
- catalog
- skill
- skillset
- workflow
[System-defined parameters]
System-defined parameters that can be used with Ops I are as follows.
(Table) System-defined parameters that can be used with the template function
| System-defined parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| .System.domain | Ops I environment domain |
Ensure that the chapter structure used in the YAML file is in the following format.
"{{.System.domain}}"
'{{.System.domain}}'
<YAML files that can use parameters>
- application
- ui
- library
- catalog
- statement (only when authzType is "uri")
- notifcation
- skill
- skillset
- workflow
Chapter structure
6.1 Workflow
6.2 UI
6.3 Datamodel
6.4 Catalog
6.5 Script
6.6 Library
6.7 Attachment
6.8 Distribution
6.9 ACL, Statement
6.10 Notification, Notifier
6.11 Application
6.12 Skill, Skillset
6.13 Calendar