4.3.11 Knowledge management
The knowledge function enables you to accumulate insights and expertise gained through the processes of failure response and inquiry handling. Those insights and expertise can be accumulated as knowledge articles and used to resolve issues that might arise.
You can categorize knowledge articles and rate those articles in terms of usefulness, so you will be able to use those articles efficiently. You can also implement access control on knowledge articles to grant access rights to specific users.
Before using the knowledge function, consider the following:
(Table) Knowledge management design items and outline
| Item | Means for definition | Key points in design |
|---|---|---|
| • Role-based display and operation permissions | GUI | Examine roles to be assigned to users according to operations on knowledge articles. |
| • Category management • Validity of categories (display/hide) |
ITSM application | Examine content-based classification of knowledge articles and category structure for access control. Create, edit, or delete categories. Examine whether to display categories in the knowledge application. |
| • Knowledge article management • Validity of knowledge articles (display/hide) • Status management of knowledge articles |
ITSM application | Create, edit, or delete knowledge articles and register file attachments.. Consider whether to display knowledge articles in the knowledge application. In addition, consider whether to make them available to customer users and requester users. |
| • Customer-based access control • Group-based access control |
GUI ITSM application |
Consider the customers and groups to be assigned to categories. |
| • Import/export | ITSM application | Import and export knowledge articles and categories (for example, performing a migration from a testing environment to a production environment.) |
(1) Outline of the Knowledge function
The application and permissions required for using the knowledge function differ depending on the operation that you want to perform.
Knowledge function operations are mainly performed in the ITSM application. Operations on ITSM applications and similar items (as indicated by red arrows in “(Figure) User operation permissions”) are applicable to all categories and knowledge articles.
Operators using the knowledge function use ITSM applications to configure access control (for example, to specify the knowledge articles that will be published or the persons who can view the articles). For details on access control, see “Access control of knowledge articles”.
Knowledge applications are mainly used to view categories and knowledge articles. Operations on knowledge applications and similar items (as indicated by blue and green arrows in “(Figure) User operation permissions”) are applicable to categories and knowledge articles that users wishing to view them have access to.
Relationships between users and applications are described below.
(Figure) User operation permissions
The meaning of each user is explained below. The terms enclosed in parentheses indicate the pre-installed roles associated with users.
- Requester User:
User of a business system. Submits applications or inquiries from the Ops I service portal or knowledge application. - Customer User:
User of the customer operation system, which is a business system. Submits applications or inquiries from the Ops I service portal or knowledge application. Can view only the knowledge articles of the same customer. - Operation Management Office Agent:
Ops I system administrator. Handles submitted applications and inquiries and creates knowledge articles. - Service Desk Agent:
Service desk representative. Responds to inquiries from requester users and customer users. - Ops I Agent (System Administrator):
Agent responsible for improving Ops I operations. Creates a service portal from an Ops I site application.
The following are applications used to perform knowledge management operations, panels used to move to applications, and windows. Detailed information about the operations is accessible from the Details column.
(Table) Applications and similar items that can be used to perform knowledge management operations
| Applications and similar items | Knowledge function | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| ITSM application | <Knowledge article> Search, viewing, creation, editing, deletion, registration/downloading of file attachments, import/export, rating*1 <Category> Creation, editing, deletion, access control, import/export |
"JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User's Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)"
|
| Knowledge application | <Knowledge article> Searching, viewing, downloading file attachments, rating |
Knowledge |
| Site application*2 | Embedding the Ops I window in a site Main sites/template sites |
|
| Chat panel (Co-Operator chat panel) |
<Knowledge article> Search The following operations can be performed on the destination application*3: <Knowledge article> Viewing, creating, registering/downloading file attachments, rating |
Basic window structure AI extension function |
| Ticket zoom window | The following operations can be performed on the destination application*4: <Knowledge article> Creating, registering file attachments |
Ticket zoom window |
(2) Access control of knowledge articles
Knowledge articles that can be displayed by a knowledge application differ depending on the settings on knowledge articles and categories, as well as the customer and group specified for the category to which the knowledge articles belong. You must use an ITSM application to make settings on knowledge articles and categories.
The following methods can be used to implement access control on knowledge articles:
- Validity of knowledge articles (display/hide)
- Status management of knowledge articles
- Validity of categories (display/hide)
- Category separation by customer
- Category separation by group
 Note
Note
In the ITSM application, you can perform operations on knowledge articles and categories for all customers and groups. Therefore, if you want to specify access control individually, you should carefully check the target customer and group.
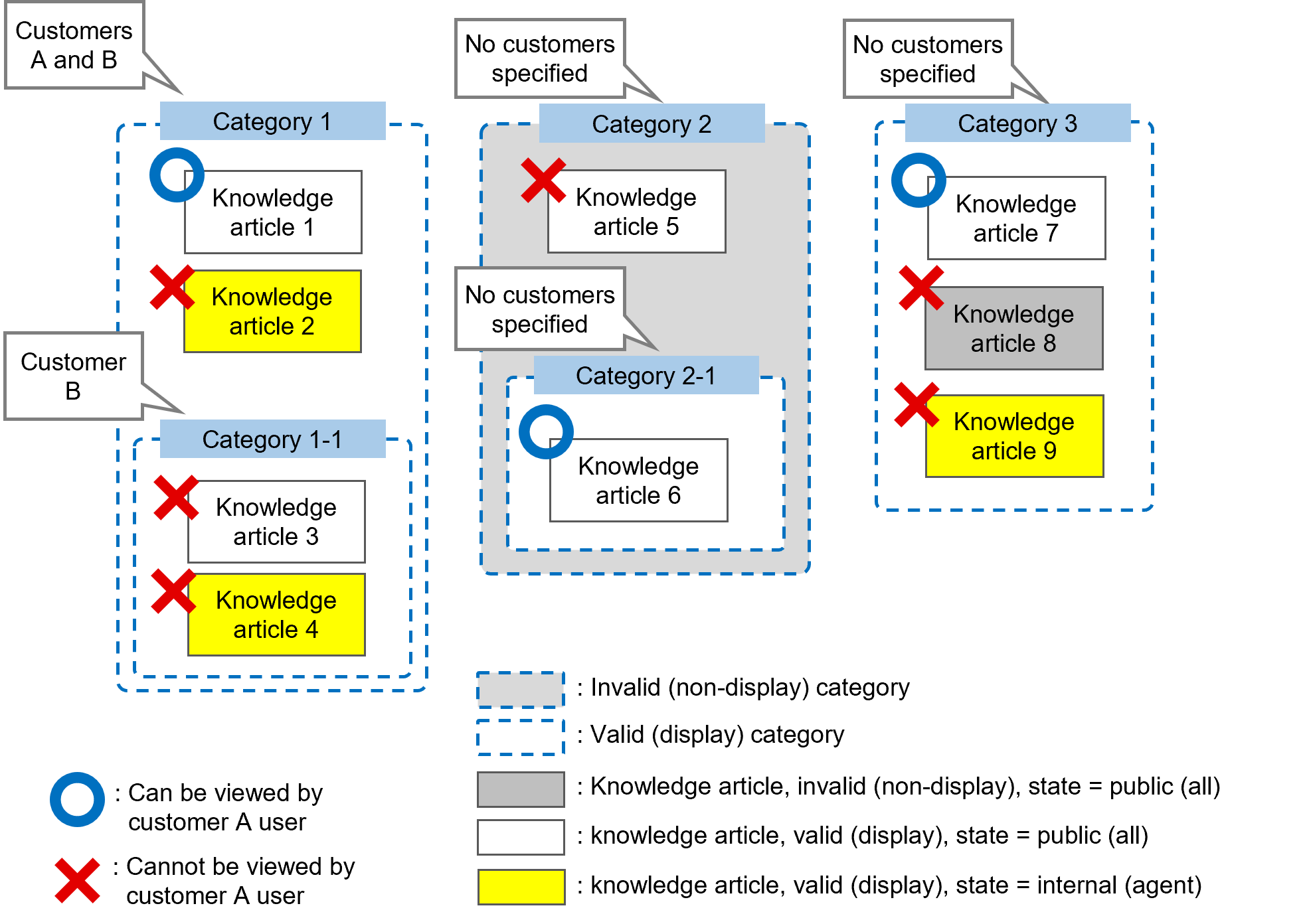
(Figure) Access control based on customer segregation, validity, and status
- Validity of knowledge articles (display/hide)
Specify "valid" if you want to display knowledge articles in the knowledge application. Specify "invalid" if you do not. Note, however, that knowledge articles specified as being invalid will be displayed for article creators.
For details on the specification method, see "[FAQ] > [New]" in "JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User's Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)". - Status management of knowledge articles
You can specify the publishing destination as "internal (agent)" or "public (all)" for each knowledge article. If "internal (agent)" is selected, the article is published to destinations other than requester users and customer users. If you want to publish an article to requester users and customer users, select "public (all)". For details on the specification method, see "[FAQ] > [New]" in "JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User's Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)". - Validity of categories (display/hide)
Specify "valid" if you want to display categories in the knowledge application. Specify "invalid" if you do not. Note, however, that categories specified as being invalid will be displayed for category creators.
Invalidating a category applies to only the category that was invalidated. It does not affect the lower-level categories. In the knowledge application, only valid categories are displayed, starting from the highest level. For details on the category specification method, see "[FAQ] > [Category Management]" in "JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User's Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)". - Category customer segregation
This control is valid for customer users.
If a customer is specified, this is displayed for non-customer users and the specified customer user. If not, this is displayed for all users. For details on customer users, see "Users". For details on the method for specifying customers for categories, see "[FAQ] > [Category Management]" in "JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User's Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)".
(Table) Access control based on customers
User Customer associated with category No settings Specify customer A Specify customers A and B Non-customer users Display Display Display Customer users belonging to customer A Display Display Display Customer users belonging to customer B Display Hide Display
- Category group segregation
This control is valid for all users.
If a group is specified, this is displayed for users belonging to all or some of the specified groups. If not, this is displayed for all groups. For details on groups, see "Groups". For details on the method for specifying groups for categories, see "[FAQ] > [Category Management]" in "JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User's Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)".
(Table) Access control based on groups
User Group associated with category No settings Specify group A Specify groups A and C Users belonging to group A only Display Display Display Users belonging to group B only Display Hide Hide Users belonging to groups A and B Display Display Display Users belonging to all the registered groups can view all the knowledge articles.
 Note
Note
- Knowledge articles cannot belong to multiple categories. If you want to publish knowledge articles to a broader audience, you should prepare, for example, a category for publishing without specifying access control for groups or customers, and register knowledge articles in that category.
- If you apply access control for both customers and groups, users who meet both conditions will have access.
- You can delete only the categories that are not associated with any knowledge articles.
- Permission settings on categories are made independently in principle, so those settings do not affect lower levels. However, if "Inherit the Customer and User group from the parent category" is checked, the permissions are inherited to lower levels in the same fashion. You can confirm whether it is checked by looking at the editing window for category management. For details, see "[FAQ] > [Category Management]" in "JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User's Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)".
- The setting on "Inherit the Customer and User group from the parent category" takes effect only within the range of contiguous categories. If there is an unchecked category somewhere in between the levels, no change will affect the category even if any category on or below the level is checked. For details, see "(Table) Effects of the settings on Inherit the Customer and User group from the parent category".
(Table) Effects of the settings on Inherit the Customer and User group from the parent category
| Categories | Before change | After change (Customers A, B, and C of the parent category are deleted. Customers D and E are added) |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (parent category) | Customers A, B, and C | Customers D and E |
| Level 2 (checked) | Customers A, B, and C | Customers D and E |
| Level 3 (not checked) | Customers A, B, and C | Customers A, B, and C |
| Level 4 (checked) | Customers A, B, and C | Customers A, B, and C |
| Knowledge window display | Customers A, B, and C: All categories can be viewed |
Customers A, B, and C: Only levels 3 and 4 can be viewed; levels 1 and 2 are not displayed. Customers D and E: Only levels 1 and 2 can be viewed; levels 3 and 4 are not displayed. |
[Category configuration use cases]
The basic principles of category configuration are shown below, along with examples of settings.
Basic principles:
- Categories at the uppermost level should be classified by service or function.
- They should be applied to subcategories of services or functions in categories at lower levels.
- The necessary customer segregation and group segregation should be set to each category.
<Examples>
- If you want to publish to an audience other than customer users (in a category):
- Create an Ops I group.
- Associate users other than customer users with the group created in a.
- Create a category.
- Set the group created in a to the category created in c.
- If you want to make "Service A" available to all customers and make "Service A-1", which is part of the Service A functions, available to "Customer X" only:
- Create categories A and A-1.
- Specify A as the parent category of A-1.
- For category A-1, clear the checkbox "Inherit the Customer and User group from the parent category" and specify customer X.
- Change the status of knowledge articles (FAQ articles in OTOBO) in categories A and A-1 to "public (all)".
(3) Importing and exporting knowledge articles and categories
You can import and export knowledge articles and categories.
CSV files are used to import and export information. CSV files can also be used to input and import information about services other than Ops I.
(Figure) Importing and exporting knowledge articles and categories


In order to perform the import or export, you need a template in which input/output items and conditions are specified.
Ops I provides the following built-in templates:
- Overwrite FAQ articles (Built-in template): For updating knowledge articles
- Add FAQ articles (Built-in template): For creating knowledge articles
- Add categories (Built-in template): For creating categories
You can edit and use the built-in templates as needed. You can also create new templates.
For details on creation and update methods, templates, and use cases, see “[FAQ] > Import/export” in “JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User’s Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)”.
[Order of import]
If an attempt is made to import knowledge articles or categories from a lower level earlier than categories from an upper level, an error occurs and the attempt fails. They must be imported from the upper level. If one CSV file is used for simultaneous import, the import is performed in sequential order from the first line to subsequent lines. In the CSV file, the objects you want to import earlier must be specified earlier than the other objects.
[Import/export restrictions and error handing]
- For import, the maximum size for CSV files is 500 MB. For export, CSV files exceeding 500 MB can be exported. If you want to import the exported CSV file as is, adjust the file size to be within 500 MB.
- The recommended number of categories or FAQ articles to be imported or exported from one CSV file is 700 or less.
- Import/export times out after 30 minutes. If it times out, follow the following instructions:
- Export: Specify search conditions and split and export the categories or FAQ articles.
- Import: Even if it times out, the processing might continue internally. Check the knowledge articles and categories after a moment and retry the import of those that have not been imported.
- If the CSV file includes knowledge articles and categories containing elements that cannot be imported, the other knowledge articles and categories, which have no problems, will be imported.
- If one or more categories are successfully imported, the category import summary displays the number of categories that are imported and the number of categories that are not imported. If the import itself fails, the cause of the error will be displayed. You can view detailed information about partial imports and import failures by selecting [Admin] from the main menu of the ITSM application and then selecting [Administration] - [System Log]. The number of displayed logs is approximately 200, so you should check the logs immediately after the import finishes.
If there are knowledge articles and categories that could not be imported, you should identify those articles and categories, identify the cause of the failure, correct it, and retry the import.
 Note
Note
- If you want to update categories by importing, you must clear the checkbox "Do not update existing Category". You must also ensure perfect matching of names including hierarchy levels (for example, upper-level category name::import target category name). If they do not match, the results are as follows:
- If the import target category name does not exist: The category will be imported as a different category.
- If the upper-level category name does not exist: An error occurs. The category will not be imported.
- If the upper-level category name is the name of another existing category: The category will be imported to the other category.
- If you export a knowledge article with multiple file attachments, it will be written in different columns with different attachment files. If you want to import a knowledge article with multiple file attachments from another service, add entries with different file attachments to different columns in the CSV file. For details on the CSV file format, see "[FAQ] > Import/export" in "JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User's Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)".
- The FaqNumber of a knowledge article is a unique number that is automatically assigned. If a new knowledge article is added to the migration source environment or the migration destination environment, the FaqNumber of the same knowledge articles might not match. If you want to update an article by importing, correct the FaqNumber so that the numbers match.
(4) Other functions
[Rating function]
If you are a viewer of knowledge articles, you can rate knowledge articles in terms of usefulness. To rate articles, use the [Knowledge Article] window of the knowledge application. You can rate the same article as many times as you want.
When you search knowledge articles in the knowledge application, you can specify a rating score as a filtering condition. For details, see “Knowledge” and “[FAQ] > FAQ Zoom screen” in “JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User’s Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)”.
 Note
Note
You can also rate articles on the FAQ Zoom screen of the ITSM application. The ITSM application does not allow the same user to update ratings, so we recommend that you rate articles in the knowledge application.
[Attaching files to a knowledge article]
You can attach multiple files to a knowledge article. The total size of files that can be attached to one knowledge article is 40 MB. You must use the ITSM application to attach files. For details, see “[FAQ] > [New] or FAQ Zoom screen” in “JP1 Cloud Service/Operations Integration User’s Guide (ITSM Operation Manual)”.
You can download attached files from the [Knowledge Article] window of the knowledge application. For details, see “Knowledge”.
[Specifying the URL of a knowledge article]
Each knowledge article has a unique URL assigned. You can directly access a knowledge article by referencing the URL. By pasting the URL to an email or work note of a ticket, you can share the knowledge article for reference.
The knowledge article URL differs between the knowledge application and the site application. For details on the URL for the knowledge application, see “Knowledge”. For details on the URL for the site application, see Embedding the Ops I window in a site.